Table of Contents
Why you need this article
Connection problems can be due to a variety of reasons: problems with the website, your device, the Wi-Fi router, modem, or your Internet Service Provider (ISP). If you can’t get email, browse the web, or stream music, chances are you’re not connected to your network and can’t get onto the internet. You may also have problems accessing shared drives or experiencing slow speeds, and this article will guide you through verifying your hardware is fully operational and hopefully point to the potential culprit.
Before you begin
When you’re starting the troubleshooting process, check all your hardware to make sure it’s connected properly, turned on, and working. If a cord has come loose or somebody has switched off an important device, this could be the problem behind your networking issues. There’s no point in going through the process of troubleshooting network issues if all you need to do is plug a cord in. Make sure all switches are in the correct positions and haven’t been bumped accidentally.
Next, turn the hardware off and back on again. This is the mainstay of IT troubleshooting, and while it might sound simplistic, often it really does solve the problem! Power cycling your modem, router, and PC can solve simple issues, just be sure to leave each device off for at least 60 seconds before you turn it back on.
Where to start
- Check for blinking lights on network port on rear of system (also check the router for blinking lights)
- Try another CAT5/Ethernet cable
- Try the same cable into another computer
- Plug your system into a different port on the router or switch
- Compare your version to the current release from Microsoft
- Try connecting directly into the modem, skipping the router for now
Windows Network Diagnostic
The Windows Troubleshooting process assists users in diagnosing and, when possible, resolving network connectivity issues.
1. Right click the Start button then select Settings>Network & Internet>Status
2. Under the Change your network settings heading, select “Network troubleshooter”
3. Follow the steps in the troubleshooter, and see if that fixes the problem
Network Settings
There are a number of different network settings that could be causing these issues. We suggest performing the following steps to verify your network settings:
Check your WiFi SSID and password
- Make sure that the network you are connecting to is the one you want, and try connecting from another device (computer/phone) to verify the password is what you think
- Now see if a Wi-Fi network you recognize and trust appears in the list of networks. If it does, select the Wi-Fi network, and then try to connect to it. If it says “Connected” underneath the network name, select Disconnect, wait a moment, and then select Connect again
- Try connecting to a network on a different frequency band. Many consumer Wi-Fi routers broadcast at two different network frequency bands: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. These will appear as separate networks in the list of available Wi-Fi networks. If your list of available Wi-Fi networks includes both a 2.4 GHz network and a 5 GHz network, try connecting to the other network
Check your DHCP settings
This one is a little more involved but equally important.
1. Select the Start button and type “Network Connections” – Select the first result
You should see something like the following but it may look different depending on your hardware. This system does not have WiFi capabilities but yours may
2. Double click your active network connection and in the new window select “Properties”
3. Click on the “Internet Protocol Version 4” option and click the “Properties” button
Likely you want DHCP enabled (unless your ISP/router requests otherwise) so make sure “Obtain an IP address automatically” is selected, as well as “Obtain DNS server address automatically”
If you wish to disable DHCP and enter your network settings instead, select the "Use the following IP address" option and enter values for IP address, Subnet mask, and Default Gateway. Also, select the "Use the following DNS server address" option and enter a value for Preferred DNS server. You can also enter a value for Alternate DNS server if you want but it is not required.
Verify Anti-Virus(AV) and Anti-Malware tools
Launch whichever AV/Anti-Malware software you use and double check to make sure it is running correctly. Verify they haven’t flagged anything that could be affecting part of your network or stopping it from functioning altogether. You may need to obtain advice from your AV manufacturer for this step.
You can also try temporarily disabling any AV/Anti-Malware software as a diagnostic step

Physical Button
If you are using a Puget laptop, we include a physical button. Make sure the physical Wi‑Fi switch on your laptop is turned on. (An indicator light usually shows when it’s on)
Commands to run
If none of the above solves your problem and if the WiFi/Wired icon appears on the right side of the taskbar with a “Connected” status, visit a different website. If the website opens, there might be a problem with the specific website. If you can’t connect to another website there are some commands we can run to check if there is a problem with the connection to your router.
1. Right click the Start button then select “Windows PowerShell”
2. In the new window type:
ipconfig /all3. Look for the name of the network you are troubleshooting and then find the IP address listed next to Default gateway for that network connection. The Default Gateway is your router’s IP. Your computer’s IP address is the number next to “IP Address.” If your computer’s IP address starts with 169, the computer is not receiving a valid IP address. If it starts with anything other than 169, your computer is being allocated a valid IP address from your router. Write down the Default Gateway address if you need to. For example: 192.168.1.1
4. In the same window type:
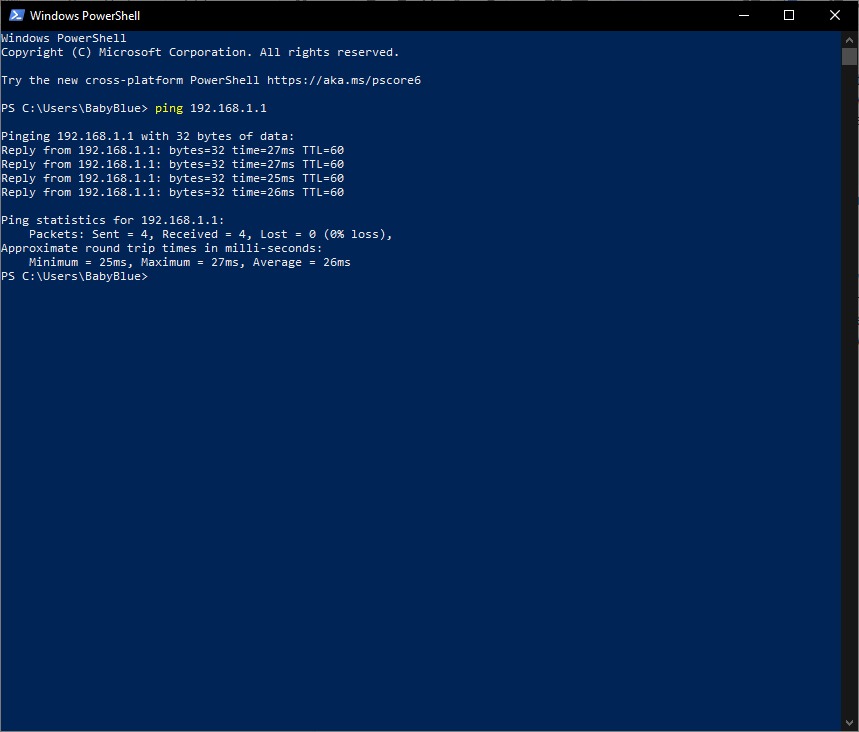
ping 192.168.1.1Replace 192.168.1.1 with YOUR default gateway
Resetting the local network connection can frequently solve connection issues. To do this type each command then hit enter in the still open PowerShell window:
ipconfig /releaseHit Enter
ipconfig /renewHit Enter
This will clear your current IP and request a new one from the router. If you still aren’t getting a valid IP or stable network connection, it may be something outside of the Puget computer causing the problem. Try plugging your computer directly into the modem using an Ethernet cable. If it works, the problem lies with the router and likely needs to be repaired or replaced.
If your router is working fine, and you have an IP address starting with something other than 169, the problem’s most likely located between your router and the internet. At this point, it’s time to use the ping tool. Try sending a ping to a well-known, large server, such as Google, to see if it can connect with your router.
You can ping Google DNS servers in the same PowerShell window by typing:
ping 8.8.8.8You can also add a “-t” modifier to the end (ping 8.8.8.8 -t) to get it to keep pinging the servers while you troubleshoot
If the pings fail to send, Windows PowerShell will return basic information about the issue.
You can use the tracert command to do the same thing by typing:
tracert 8.8.8.8This will show you each step, or “hop,” between your router and the Google DNS servers. You can see where along the pathway the error is arising. If the error comes up early along the pathway, the issue is more likely somewhere in your local network
SafeMode
Reboot the system in “Safe Mode with Networking” and try replicating the issue. Safe mode disables all background software and services. With these software/service items disabled, diagnosing can more effectively be narrowed down to hardware.
Updating network drivers
This will guide you through performing an update of your network drivers using Device Manager.
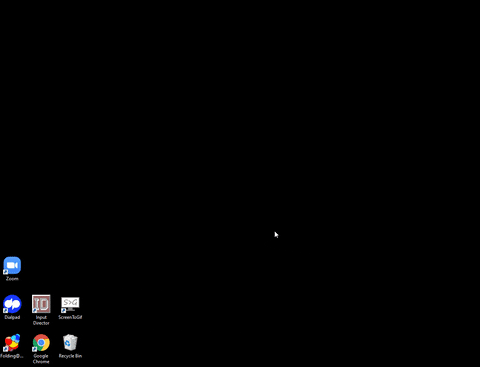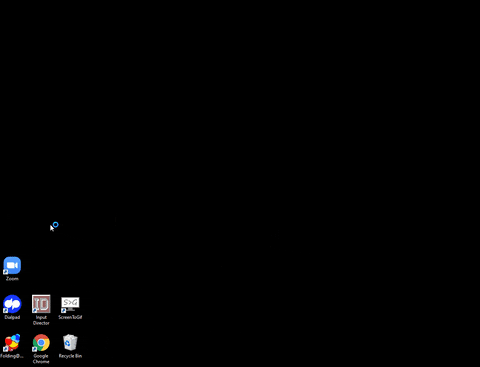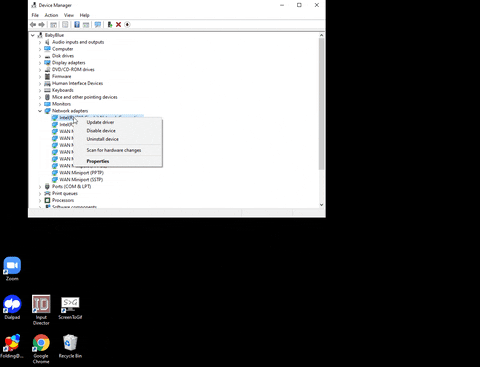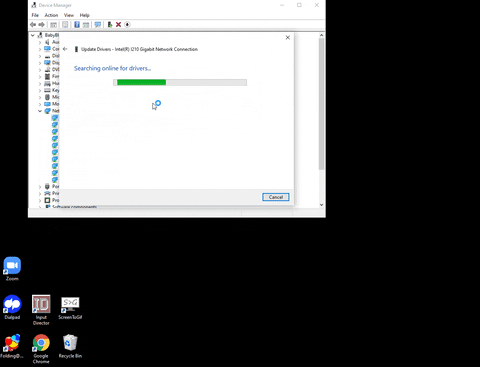
1. Right click on the Start Button
2. Select “Device Manager”
3. Click the “Network Adapters” caret
4. Right click the adapter you would like to work on and select “Update”
5. Select “Search automatically for updated driver software” then let it do what it does
Complete Internet Repair (CIntRep)
With internet or networking issues in Windows, the cause can sometimes be traced to a Windows setting that has been corrupted. To help with that, we typically recommend running a utility called Complete Internet Repair. (CIntRep)
The Support department occasionally utilizes this tool as it automates a lot of the above. It is not the most straightforward tool so feel free to reach out with your order number and our Support team can help guide you through.
These are the basic instructions/recommendations:
You’ll need to download it to another system then copy the file (ComIntRep_####_Setup.exe) to a flash drive. Transfer the flash drive to the affected system and copy the file to an easy to find location. Launch the application and follow the prompts to install: Accept the license agreement, create shortcuts for easy access then click “Install”. Once it finishes installing, check the box for “Launch Complete Internet Repair” and uncheck the box for “Visit Rizonesoft for more downloads”.
Select the following options for typical solutions:
- Reset Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) (removes and re-adds the protocol)
- Repair Winsock (resets the catalog)
- Renew Internet Connections (release and renew all tcp/ip Internet Connections)
- Flush DNS Resolver Cache (refresh all DHCP leases and re-register DNS names)
In addition, if any of the other options look like they could apply to you, you can mouse over the icon on the left and it will tell you more about what it will do, then you can select them as well. Click “GO” then once it runs, you will need to restart your computer.
Conclusion
All of these network troubleshooting tips are designed to guide you through verifying settings are correct and hardware is operating as expected. If all of the above turn up no problems, try contacting your internet service provider to see if they’re having issues. You can also look up outage maps and related information on a smartphone to see if others in your area are having the same problem.
DownDetector.com is a great site for checking if there is an outage in your area or directly related to your provider.
Need help with your Puget Systems PC?
If something is wrong with your Puget Systems PC. We are readily accessible, and our support team comes from a wide range of technological backgrounds to better assist you!
Looking for more support guides?
If you are looking for a solution to a problem you are having with your PC, we also have a number of other support guides that may be able to assist you with other issues.